
Ear infections might be common, but they’re far more serious than many people realize. An ear infection occurs when a viral or bacterial infection causes inflammation and fluid buildup in the ear. Middle ear infections (otitis media) are the most common form of infection.
However, infections can occur in the outer, middle, or inner part of the ear. Symptoms can vary depending on the specific part of the ear affected, ranging from mild discomfort to more serious pain and even hearing loss, both temporary and permanent.
In this guide, we explore the different kinds of ear infections and their potential impact on hearing health.
Types of Ear Infections
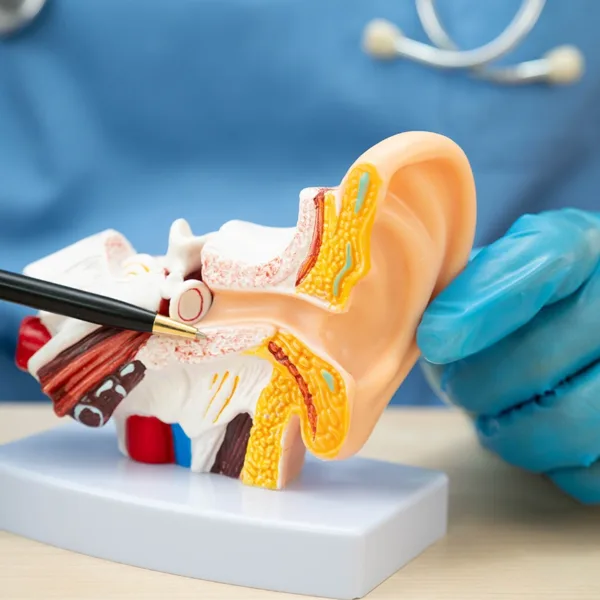
An ear infection is inflammation and fluid buildup in the outer, middle, or inner ear. These three sections of the ear each play a unique role in hearing and balance:
- Outer Ear: The visible part of the ear that funnels sound waves down the ear canal.
- Middle Ear: The area behind the eardrum that contains the tiny bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations.
- Inner Ear: The space that houses the auditory nerve, cochlea (responsible for hearing), and the vestibular system (responsible for balance).
Where the infection occurs in the ear determines what kind of ear infection it is and what symptoms it causes. Below we list the three main types of ear infections, their most common causes, symptoms, and treatment options:
Outer Ear Infection or “Swimmer’s Ear” (Otitis Externa)
An outer ear infection (otitis externa), also known as “swimmer’s ear,” is a common infection caused by bacteria or fungal growth in the ear canal. It can cause significant ear pain, often accompanied by redness, swelling, itching, or greenish discharge.
The most common causes of an outer ear infection include:
- Swimming: swimming in contaminated water can cause bacteria to infect the ear canal.
- Cotton swabs: using cotton swabs can create tiny abrasions that allow bacteria and fungi to grow, especially when combined with moisture from sweating, showering, or swimming.
- Skin conditions: conditions like eczema or psoriasis can damage the protective skin barrier inside the ear, causing inflammation, flakiness, and less earwax. This can create an environment for bacteria and fungi to grow, often worsened by moisture.
Treatments for an outer ear infection depend on whether the infection is bacterial or fungal. In many cases, antibiotics and pain medicine can relieve symptoms within a few days to a week.
Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media)
A middle ear infection (otitis media) affects the space behind the eardrum and is the most common type of ear infection. Research shows that nearly 80% of all children will experience a middle ear infection at least once.1
Middle ear infections are most commonly caused by viruses or bacteria and can be triggered by colds or allergies.
Common symptoms of middle ear infections include:
- Ear pain
- Feeling of fullness in the ear
- Dizziness or imbalance
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Yellow or bloody discharge
Some viral infections can heal on their own within 3-5 days. However, middle ear infections typically require antibiotics to be treated. If a middle ear infection goes untreated, recurs, or leads to complications, it can cause permanent damage and hearing loss.
Inner Ear Infection (Labyrinthitis or Vestibular Neuritis)
Inner ear infections are less common, but very serious. They are usually caused by viruses like the flu (influenza), common cold, Epstein-Barr, and COVID-19.
The inner ear houses the two systems responsible for balance and hearing, so when it becomes infected, it often affects both at the same time. This can lead to symptoms like vertigo, nausea, tinnitus, and hearing changes.
There are two main types of inner ear infections, including:
- Labyrinthitis: inflammation in the cochlea (which enables hearing)
- Vestibular neuritis: inflammation in the vestibular nerve (which helps you balance)
Since inner ear infections are mainly caused by viruses, treatment may involve antiviral medications or pain relievers to manage symptoms.
How Ear Infections Can Affect Your Hearing
Ear infections can interfere with your hearing in several ways, depending on the cause, severity, and where it occurs. While some hearing changes are temporary and resolve once the infection clears, others may cause lasting damage if left untreated.
Below are some of the main ways that ear infections can impact hearing:
Fluid Buildup
Infections in the outer or middle ear can cause fluid buildup that blocks sound from traveling efficiently to the inner ear. Sounds may seem muffled, quiet, or distorted, similar to having water in your ears.
While hearing changes usually resolve once the infection clears, if left untreated, fluid buildup can cause the eardrum to rupture, potentially leading to permanent hearing damage. We cover this in depth below.
Eardrum Damage or Perforation
Severe or untreated middle ear infections can cause pus or fluid buildup that increases pressure behind the eardrum. Sometimes this pressure can be so severe that it ruptures the eardrum, causing sudden hearing loss.
While eardrums can heal on their own, repeated ruptures or scarring can cause long-term damage and hearing loss.
Ear Inflammation and Swelling
Ear infections can cause inflammation and swelling inside the ear. This can block sound and make noises seem muffled or quiet. The effect can be temporary and often goes away when the infection is treated.
However, chronic inflammation can cause damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, resulting in permanent hearing loss. The longer the inflammation lasts, or the more frequently it occurs, the more damage it can cause, greatly increasing the risk of hearing loss.
Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma is a noncancerous skin cyst that develops in the middle ear behind the eardrum, often resulting from recurring middle ear infections. This condition does not go away on its own and often requires surgery to remove the growth.
Without timely intervention, cholesteatomas can lead to even more serious problems like meningitis, brain infection, or permanent hearing loss.
Meningitis
Meningitis is when the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord become inflamed. This condition can be caused by viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infections, and in some cases is a severe complication of a middle ear infection.
When an ear infection spreads to nearby structures in the head and causes meningitis, this inflammation can damage the auditory nerve, leading to permanent hearing loss. Research shows that hearing loss is reported in about 54% of people who experienced meningitis.2
Find The Personalized Hearing Care You Deserve at Audibel
Ear infections are common, but their effects have a greater impact than many people realize. Outer, middle, and inner ear infections can all lead to irreversible hearing loss without proper treatment.
At Audibel, our hearing care professionals are dedicated to supporting your hearing health for the long term. Whether you’re experiencing hearing changes after an ear infection or simply need a routine check-up, our specialists are here to help. Find an Audibel clinic near you to get the hearing care you deserve.
References
- Danishyar, A., & Ashurst, J. V. (2023b, April 15). Acute otitis media. StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470332/
- Jensen, E. S., Cayé-Thomasen, P., Bodilsen, J., Nielsen, H., Friis-Hansen, L., Christensen, T., Christiansen, M., Kirchmann, M., & Brandt, C. T. (2023b). Hearing Loss in Bacterial Meningitis Revisited—Evolution and Recovery. Open Forum Infectious Diseases, 10(3), ofad056. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofad056






Have a question or Comment?